Performance, Security, and Usability Testing
by Srinesh Nisala (Senior Software Engineer @ iLabs)
- LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/srinesh-nisala/
- GitHub: https://github.com/s1n7ax
Pre-requisites
- Basic understanding of software testing concepts
- Familiarity with web applications and APIs
- Access to a computer with internet connection for tools setup
Module Overview
This module covers three critical aspects of software testing:
- Performance Testing - Load testing with JMeter
- Security Testing - OWASP Top 10 fundamentals
- Usability Testing - Principles and heuristics evaluation
Part 1: Performance Testing with JMeter
Anton Putra has comprehensively covered performance testing in his YouTube series. https://www.youtube.com/@AntonPutra
What is Performance Testing?
Performance testing evaluates how well a system performs under various conditions:
- Load Testing: Normal expected load
- Stress Testing: Beyond normal capacity
- Spike Testing: Sudden load increases
- Volume Testing: Large amounts of data
JMeter Introduction
Apache JMeter is an open-source tool for performance testing:
- Java-based application
- GUI and command-line modes
- Supports various protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, JDBC, etc.)
Quick JMeter Setup Demo
# Download and extract JMeter
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/jmeter/binaries/apache-jmeter-5.6.2.zip
unzip apache-jmeter-5.6.2.zip
cd apache-jmeter-5.6.2/bin
./jmeter.sh
JMeter Load Testing Demo
-
Thread Group: Simulates users
- Number of threads (users)
- Ramp-up period
- Loop count
-
HTTP Request Sampler: Defines the request
- Server name/IP
- Port number
- Method (GET, POST, etc.)
- Path
-
Listeners: View results
- View Results Tree
- Summary Report
- Graph Results
Part 2: Security Testing Fundamentals - OWASP Top 10
OWASP Top 10 Overview
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 represents the most critical security risks:
1. Broken Access Control
Facebook Privileged (De)-escalation vulnerability
- Risk: Users can access unauthorized functionality
- Causes:
- Missing access control checks
- Improper role validation
- Direct object references
- Elevation of privilege vulnerabilities
- Example: Direct URL access to admin pages
- Testing: Try accessing restricted URLs without proper authentication
2. Cryptographic Failures
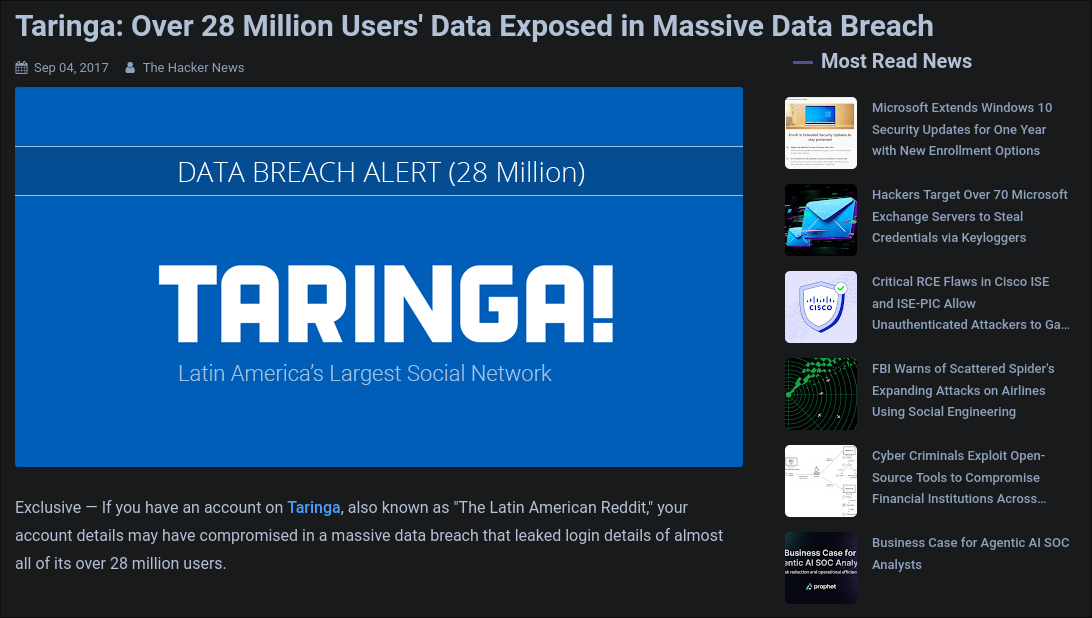

- Risk: Sensitive data exposure due to weak encryption
- Causes:
- Weak encryption algorithms
- Poor key management
- Storing sensitive data in plaintext
- Using deprecated cryptographic functions
- Example: Plain text passwords, weak hashing
- Testing: Check for HTTPS usage, password storage methods
3. Injection
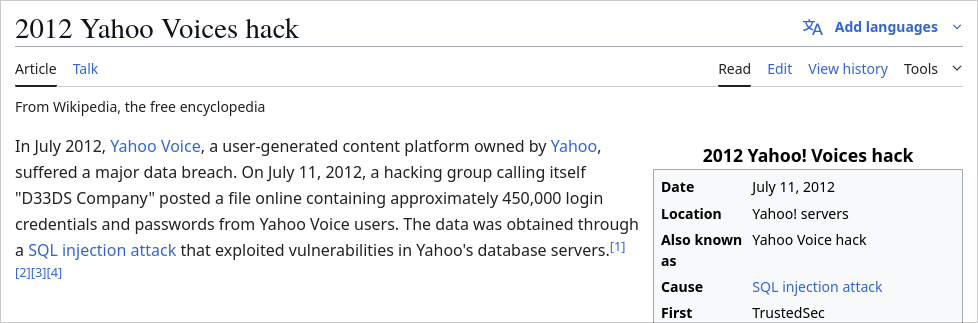
- Risk: Untrusted data sent to interpreter
- Causes:
- Lack of input validation
- Improper parameterization
- Insufficient sanitization
- Dynamic query construction
- Example: SQL injection, command injection
- Testing: Input validation with malicious payloads
query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" + username + "';"
cursor.execute(query)
Passing ' OR '1'='1 as username would return all users.
query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?"
cursor.execute(query, (username,))
4. Insecure Design
- Risk: Flawed architecture and design
- Causes:
- Missing security requirements
- Threat modeling gaps
- Inadequate security controls
- Lack of security by design principles
- Example: Missing security controls in design phase
- Testing: Review system architecture for security gaps
5. Security Misconfiguration

- Risk: Insecure default configurations
- Causes:
- Default settings left unchanged
- Incomplete configurations
- Excessive privileges
- Missing security hardening
- Example: Default passwords, unnecessary services enabled
- Testing: Check for default configurations, exposed admin interfaces
6. Vulnerable and Outdated Components
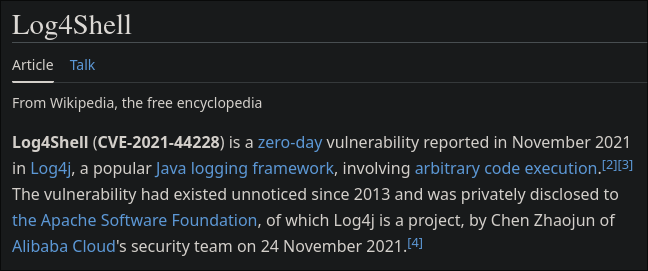
- Risk: Using components with known vulnerabilities
- Causes:
- Poor dependency management
- Lack of security updates
- Using deprecated components
- Insufficient vulnerability monitoring
- Example: Old library versions with security flaws
- Testing: Dependency scanning, version checking
7. Identification and Authentication Failures
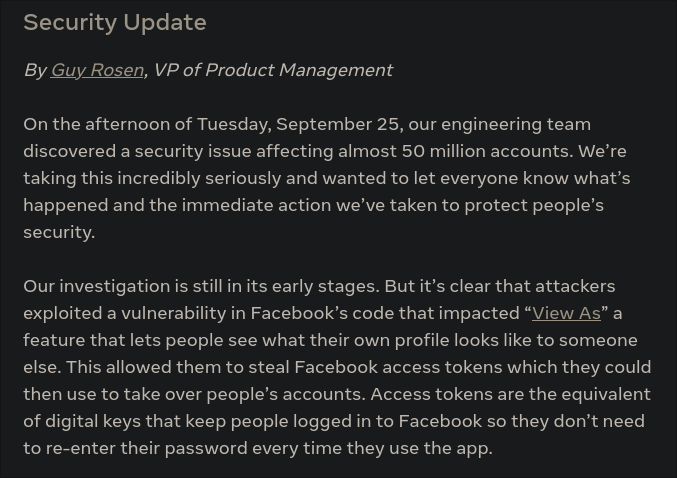
- Risk: Compromised user identity functions
- Causes:
- Weak password policies
- Insufficient session management
- Poor credential storage
- Missing multi-factor authentication
- Example: Weak passwords, session management flaws
- Testing: Brute force attacks, session hijacking attempts
8. Software and Data Integrity Failures
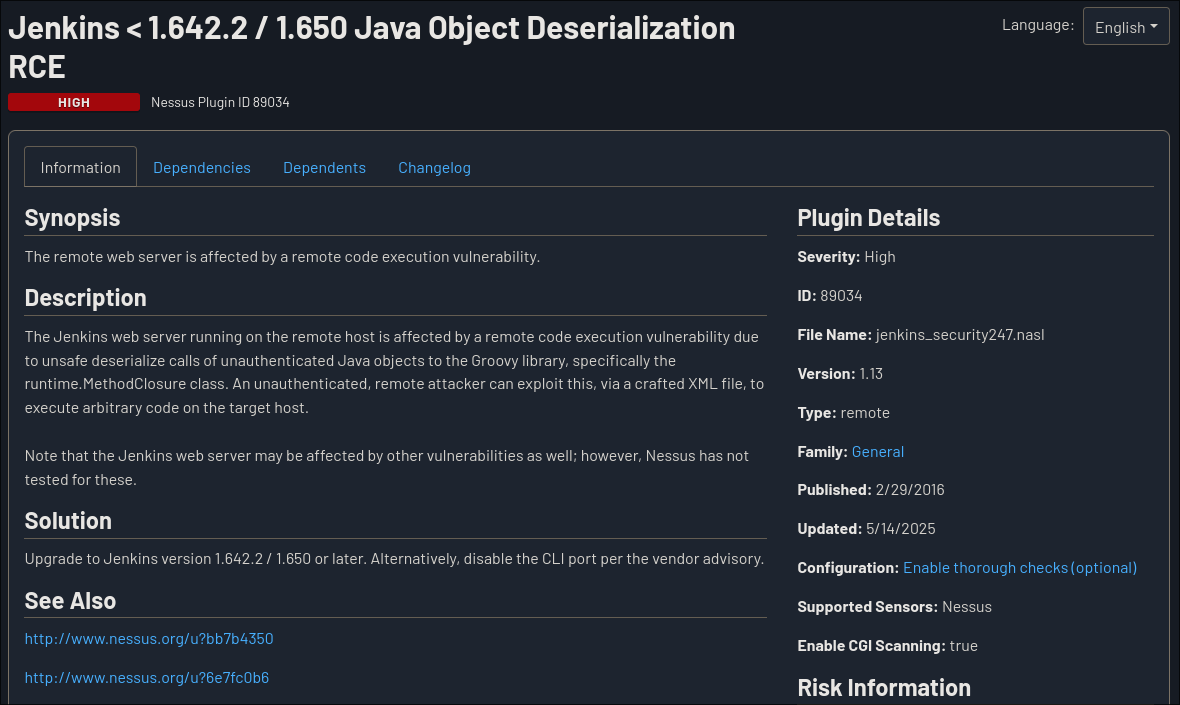
- Risk: Untrusted software updates and data
- Causes:
- Lack of integrity verification
- Insecure CI/CD pipelines
- Unsigned code
- Missing checksum validation
- Example: Unsigned software updates
- Testing: Verify software signatures, data integrity checks
9. Security Logging and Monitoring Failures

- Risk: Insufficient logging and monitoring
- Causes:
- Inadequate logging implementation
- Missing alerting systems
- Poor incident response
- Lack of log analysis
- Example: No audit logs, delayed breach detection
- Testing: Check logging mechanisms, incident response
10. Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
- Risk: Application fetches remote resources without validation
- Causes:
- Insufficient URL validation
- Lack of network segmentation
- Improper input filtering
- Missing allowlist controls
- Example: Internal network access through application
- Testing: Manipulate URLs to access internal resources
Security Testing Tools Demo
Quick demonstration of common security testing tools:
- OWASP ZAP: Web application security scanner
- Burp Suite: Web vulnerability scanner
- Browser Developer Tools: For manual testing
Manual Security Testing Example
Simple XSS test:
<script>
alert("XSS");
</script>
Part 3: Usability Testing Principles and Heuristics
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing evaluates how easy and intuitive a product is to use:
- User Experience (UX): Overall user satisfaction
- User Interface (UI): Visual and interactive elements
- Accessibility: Usability for users with disabilities
Nielsen's 10 Usability Heuristics
1. Visibility of System Status
- Keep users informed about what's happening
- Example: Loading indicators, progress bars
2. Match Between System and Real World
- Use familiar language and concepts
- Example: Shopping cart metaphor in e-commerce
3. User Control and Freedom
- Provide undo/redo functionality
- Example: Back button, cancel operations
4. Consistency and Standards
- Follow platform conventions
- Example: Consistent navigation, standard icons
5. Error Prevention
- Prevent errors through good design
- Example: Form validation, confirmation dialogs
6. Recognition Rather Than Recall
- Make information visible
- Example: Recently used items, visible options
7. Flexibility and Efficiency of Use
- Shortcuts for experienced users
- Example: Keyboard shortcuts, customizable interfaces
8. Aesthetic and Minimalist Design
- Remove unnecessary elements
- Example: Clean interfaces, focused content
9. Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Recover from Errors
- Clear error messages with solutions
- Example: Specific error descriptions, recovery suggestions
10. Help and Documentation
- Easy to find and follow help
- Example: Search functionality, step-by-step guides
Usability Testing Methods
- Moderated Testing: Researcher guides users
- Unmoderated Testing: Users complete tasks independently
- A/B Testing: Compare different versions
- Heuristic Evaluation: Expert review using heuristics
- Card Sorting: Information architecture testing
Practical Exercise Ideas (For Self-Study)
Performance Testing
- Set up JMeter and create a test plan for a public API
- Monitor system resources during load testing
- Analyze bottlenecks and performance issues
Security Testing
- Use OWASP ZAP to scan a test application
- Practice manual testing for common vulnerabilities
- Review application logs for security events
Usability Testing
- Conduct heuristic evaluation on a website
- Create user personas and scenarios
- Design usability test protocols
Tools and Resources
Performance Testing
- JMeter: https://jmeter.apache.org/
- LoadRunner: Commercial tool
- Gatling: Modern load testing tool
Security Testing
- OWASP ZAP: https://www.zaproxy.org/
- Burp Suite: https://portswigger.net/burp
- OWASP WebGoat: Practice application
Usability Testing
- UsabilityHub: Online usability testing
- Hotjar: User behavior analytics
- Figma: Design and prototyping tool
Key Takeaways
- Performance Testing: Essential for ensuring applications can handle expected load
- Security Testing: Critical for protecting user data and system integrity
- Usability Testing: Improves user satisfaction and adoption
- Integration: These testing types complement each other in comprehensive QA strategy
- Continuous Testing: Implement these tests throughout the development lifecycle